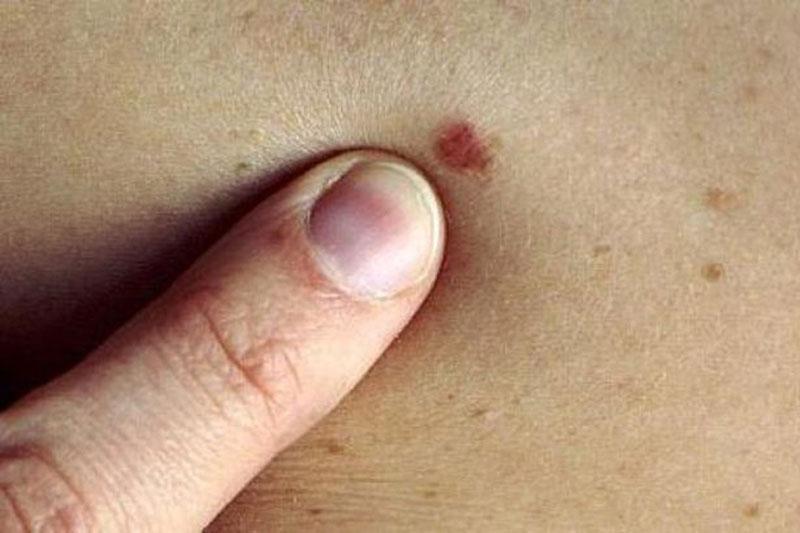
Skin cancers are serious health conditions resulting from the uncontrolled proliferation of skin cells and can manifest in various forms. Associate Professor Tuğba Falay Gür specializes in understanding the causes of skin cancers, developing early diagnosis methods, and offering effective treatment options.
Types of Skin Cancer
- Basal Cell Carcinoma (BCC)
- Squamous Cell Carcinoma (SCC)
- Melanoma
- Merkel Cell Carcinoma
- Other Rare Skin Cancers
Basal Cell Carcinoma (BCC)
BCC is the most common type of skin cancer, typically found on sun-exposed areas such as the face, ears, and neck.
Causes:
- UV Radiation Exposure: Harmful UV rays from the sun are the primary cause of BCC.
- Genetic Factors: Family history of skin cancer increases the risk.
- Skin Type: Fair-skinned individuals with blond hair and blue or green eyes are at higher risk.
- Weakened Immune System: Those with compromised immunity are more likely to develop BCC.
Symptoms:
- Red or Pink Lesions: Smooth or soft-edged patches.
- Sore-like Rash: Small, non-healing sores or blisters.
- Shiny or Reflective Surface: A glossy or mirror-like appearance on the lesion.
- Bleeding or Irritation: May bleed or become irritated over time.
Treatment Options:
- Surgical Removal: Excision of the lesion.
- Cryotherapy: Freezing the lesion using liquid nitrogen.
- Laser Therapy: Destruction of cancer cells with laser energy.
- Radiation Therapy: Targeting cancer cells with high-energy rays.
Prevention:
- Use Sunscreen: Broad-spectrum sunscreen is essential.
- Protective Clothing: Wear hats, long-sleeved shirts, and sunglasses.
- Limit Sun Exposure: Avoid being outdoors during peak sunlight hours.
Squamous Cell Carcinoma (SCC)
SCC is the second most common type of skin cancer, commonly appearing on sun-exposed areas such as the face, ears, neck, and hands.
Causes:
- UV Radiation Exposure: UV rays are a significant risk factor.
- Genetic Factors: Family history of skin cancer increases susceptibility.
- Weakened Immune System: Higher risk for individuals with compromised immunity.
- Chemical Exposure: Contact with certain industrial chemicals.
Symptoms:
- Redness and Swelling: Raised, scaly red patches.
- Cracks and Sores: Persistent, non-healing cracks or sores.
- Shiny or Soft Texture: Shiny, smooth, or flaky lesions.
- Bleeding or Irritation: May bleed or become irritated.
Treatment Options:
- Surgical Removal: Excision of the affected area.
- Radiation Therapy: Destruction of cancer cells with radiation.
- Chemotherapy: Use of drugs to kill cancer cells.
- Laser Therapy: Targeted destruction of cancer cells using laser energy.
Prevention:
- Use Sunscreen: Apply broad-spectrum sunscreen regularly.
- Protective Clothing: Wear UV-protective clothing and sunglasses.
- Limit Sun Exposure: Avoid being outdoors during peak UV hours.
Melanoma
Melanoma is the most serious type of skin cancer, originating from pigment-producing cells called melanocytes. If not detected early, it can spread rapidly and become life-threatening.
Causes:
- Genetic Predisposition: Family history of melanoma increases risk.
- UV Radiation Exposure: Sun and tanning bed use significantly heighten melanoma risk.
- Skin Type: Fair-skinned individuals with blond hair and blue eyes are more susceptible.
- Genetic Mutations: Mutations in genes like BRAF and NRAS contribute to melanoma development.
Symptoms:
- ABCDE Criteria:
- A (Asymmetry): One half of the mole doesn’t match the other.
- B (Borders): Irregular or blurred edges.
- C (Color): Multiple shades of brown, black, or other colors.
- D (Diameter): Larger than 6mm.
- E (Evolution): Changes in size, shape, or color.
- New Moles: Appearance of new moles on the skin.
- Seasonal Changes: Moles may become more prominent in summer.
- Pain or Discomfort: Itching, pain, or sensitivity in the mole.
Treatment Options:
- Surgical Removal: Excision of the melanoma lesion.
- Immunotherapy: Boosting the immune system to fight cancer cells.
- Targeted Therapy: Drugs targeting specific cancer cell mutations.
- Radiation Therapy: Using high-energy rays to destroy cancer cells.
- Chemotherapy: Medications to kill cancer cells.
Prevention:
- Use Sunscreen: Apply SPF 30+ sunscreen.
- Protective Clothing: Wear sun-protective clothing and accessories.
- Limit Sun Exposure: Avoid sun exposure during peak hours.
- Regular Mole Checks: Perform self-checks and consult a dermatologist for changes.
- Avoid Tanning Beds: Refrain from using tanning beds.
Merkel Cell Carcinoma
Merkel cell carcinoma is a rare and aggressive skin cancer affecting Merkel cells, which are located near nerve endings in the skin.
Causes:
- Genetic Factors: Family history of skin cancer.
- UV Radiation Exposure: Prolonged sun exposure.
- Weakened Immune System: Higher risk in immunocompromised individuals.
- Merkel Cell Mutations: Triggered by genetic or viral factors.
Symptoms:
- Red or Purple Nodules: Rapidly growing nodules on the skin.
- Swelling and Pain: Nodules may be swollen and tender.
- Fast-Spreading Tendencies: Quick spread to lymph nodes and other organs.
- Skin Discoloration: Color changes around nodules.
Treatment Options:
- Surgical Removal: Excision of the cancerous tissue.
- Radiation Therapy: Targeted destruction of cancer cells.
- Immunotherapy: Strengthening the immune response against cancer.
- Chemotherapy: Drugs to eliminate cancer cells.
- Targeted Therapy: Focused treatments for specific mutations.
General Prevention Measures
To prevent skin cancers, consider these strategies:
- Apply Sunscreen: Use broad-spectrum SPF 30+ sunscreen.
- Wear Protective Clothing: Shield your skin with UV-protective apparel.
- Limit Sun Exposure: Avoid peak sun hours (10:00 am–4:00 pm).
- Routine Skin Checks: Schedule regular dermatology appointments and conduct self-checks.
- Healthy Lifestyle: Maintain a balanced diet, regular exercise, and sufficient sleep.
- Avoid Tanning Beds: Refrain from using artificial tanning devices.
Appointments and Contact
For more information on skin cancers, early diagnosis through skin screenings, and expert advice, please contact us. Benefit from Associate Professor Tuğba Falay Gür’s expertise for healthy and balanced skin.