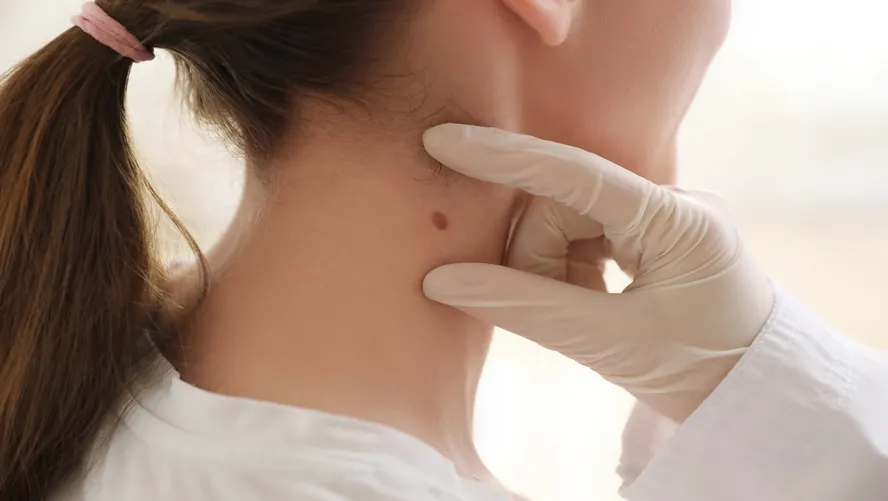
Moles are naturally occurring small spots on the skin that contain melanin pigment and are usually brown or black in color. Assoc. Prof. Dr. Tuğba Falay Gür specializes in understanding the causes of moles, monitoring them, and offering treatment options when necessary.
Causes
Various factors contribute to the formation of moles:
- Genetic Predisposition: Individuals with a family history of moles or skin cancer are at higher risk of developing moles.
- Sun Exposure: Prolonged exposure to UV rays can increase the number and size of moles.
- Hormonal Changes: Fluctuations in hormone levels during puberty, pregnancy, and hormone treatments can trigger the development of moles.
- Age: Moles are more common during childhood and adolescence; they may disappear or new ones may form as age progresses.
Symptoms
Moles are identified by their distinct characteristics:
- Color: They can be brown, black, or skin-colored.
- Shape and Size: Typically oval or round, they may be smaller or larger than 6 mm.
- Borders: Edges can be smooth and well-defined or irregular.
- Texture: The surface may be smooth or raised.
Monitoring and Observation
Regular monitoring of moles is crucial for the early detection of skin cancer. Assoc. Prof. Dr. Tuğba Falay Gür recommends the following monitoring methods:
- Regular Check-ups: Annual skin examinations are essential to track changes in moles.
- ABCDE Criteria: Used to evaluate changes in moles:
- A (Asymmetry): One half of the mole does not match the other half.
- B (Borders): Edges are irregular, scalloped, or blurred.
- C (Color): Uneven color tones or multiple colors may be present.
- D (Diameter): Moles larger than 6 mm or those growing rapidly should be monitored.
- E (Evolution): Changes in size, shape, or color over time.
Treatment Methods
Several treatment options are available for moles:
- Surgical Biopsy: Removal of suspicious moles for laboratory examination.
- Cryotherapy: Freezing the mole with liquid nitrogen to destroy it.
- Laser Therapy: Using laser beams to remove moles and improve appearance.
- Radiotherapy: Used in cases of suspected cancerous moles.
- Surgical Removal: Excision of moles with a high risk of cancer.
Prevention and Protection
To reduce the risk of mole formation and skin cancer, the following measures can be taken:
- Use Sunscreen: Apply broad-spectrum sunscreen and wear protective clothing when exposed to the sun.
- Regular Skin Checks: Conduct self-examinations of the skin regularly and note any changes.
- Avoid UV Exposure: Limit outdoor activities during peak sunlight hours.
- Skin Care: Keep the skin moisturized and avoid irritants.
Skin Care and Lifestyle
Proper skin care and a healthy lifestyle are vital for maintaining the health of moles and overall skin health:
- Gentle Cleansers: Use mild, hypoallergenic cleansers instead of harsh soaps.
- Moisturizing: Regularly moisturize the skin to protect the skin barrier.
- Healthy Diet: Consume a diet rich in vitamins and antioxidants to support skin health.
- Adequate Sleep: Sufficient sleep promotes skin renewal and overall health.
- Reduce Smoking and Alcohol Consumption: These substances can negatively affect skin health.
Appointment and Contact
For more information about moles and monitoring, and to get expert advice, please contact us using the provided details. Rely on Assoc. Prof. Dr. Tuğba Falay Gür’s expertise for healthy and aesthetic skin.