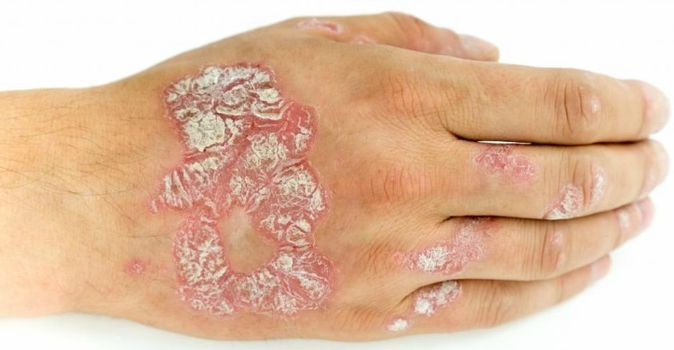
Psoriasis is a chronic and inflammatory skin condition caused by the rapid proliferation of skin cells. Associate Professor Tuğba Falay Gür specializes in understanding the causes of psoriasis, offering effective treatment options, and improving patients’ quality of life.
Causes
While the exact cause of psoriasis is unknown, several factors contribute to its development:
- Genetic Predisposition: Individuals with a family history of psoriasis are at a higher risk.
- Immune System Disorders: Autoimmune reactions cause the immune system to attack skin cells.
- Infections: Certain infections, such as those caused by streptococcus bacteria, can trigger psoriasis.
- Stress: High levels of stress can lead to psoriasis flare-ups.
- Medication Use: Beta blockers, lithium, and some anti-inflammatory drugs may worsen psoriasis.
- Skin Injuries: Cuts, burns, or other skin injuries can trigger or worsen psoriasis.
- Smoking and Alcohol Use: These habits can increase the severity of psoriasis.
Symptoms
Psoriasis manifests with various skin-related symptoms:
- Red Patches: Raised red patches commonly appear on the elbows, knees, scalp, back, and lower back.
- Scaling: Silver-colored scaling can be seen on the red patches.
- Thickened Skin: Affected areas of the skin become thick and hard.
- Itching and Discomfort: Patches may cause itching, burning, or discomfort.
- Nail Changes: Pitting, discoloration, and thickening of nails can occur.
- Joint Pain: Psoriatic arthritis, an inflammatory joint condition, can develop in individuals with psoriasis.
Treatment Options
Various treatment methods are available for managing psoriasis:
- Topical Treatments: Corticosteroid creams, retinoids, and calcineurin inhibitors control inflammation and regulate cell renewal in the skin.
- Phototherapy: UVB light or PUVA therapy promotes skin cell regeneration.
- Oral Medications: Methotrexate, cyclosporine, and biologics suppress the immune system and manage severe cases.
- Chemical Peels: These methods renew the skin surface and reduce the appearance of psoriasis patches.
- Lifestyle Changes: Reducing smoking and alcohol consumption, managing stress, and maintaining a healthy diet support treatment.
Prevention and Management
While psoriasis cannot be entirely prevented, certain measures can help prevent flare-ups:
- Sun Protection: Use broad-spectrum sunscreens to protect the skin from harmful UV rays and prevent damage.
- Stress Management: Yoga, meditation, and other stress-reduction techniques help prevent disease triggers.
- Regular Skincare: Use gentle cleansers, moisturize the skin, and avoid irritating products to maintain skin health.
- Healthy Diet: A diet rich in antioxidants and omega-3 fatty acids may reduce inflammation and strengthen the immune system.
- Avoiding Skin Injuries: Protecting the skin from cuts or burns is important as injuries can trigger flare-ups.
Skincare and Lifestyle
Effective management of psoriasis relies on proper skincare and a healthy lifestyle:
- Gentle Cleansers: Use hypoallergenic cleansers to avoid irritating the skin.
- Moisturization: Regularly hydrate the skin to maintain its barrier and reduce irritation.
- Balanced Nutrition: Consume foods rich in vitamins and antioxidants to boost the immune system.
- Adequate Sleep: Sufficient sleep supports the body’s healing processes.
- Reduce Smoking and Alcohol Consumption: These substances can weaken the immune system and exacerbate the disease.
- Stress Management: Practices like meditation, yoga, and breathing exercises support overall health and immunity.
Appointments and Contact
For more information about psoriasis and to receive expert guidance, please contact us. Enhance your skin health and achieve balance with the expertise of Associate Professor Tuğba Falay Gür.