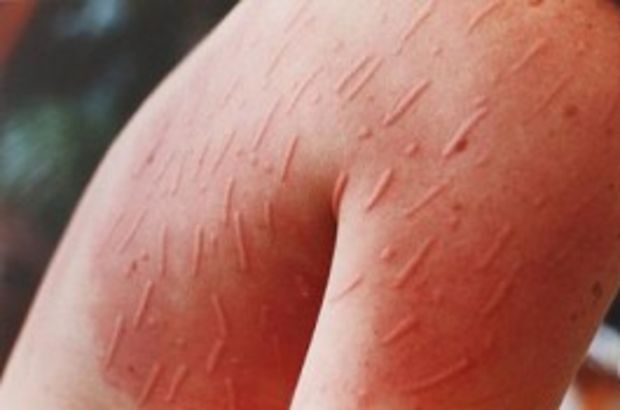
Scabies is a highly contagious skin infection caused by the microscopic mite Sarcoptes scabiei, which burrows into the skin. Associate Professor Tuğba Falay Gür specializes in understanding the causes of scabies, providing effective treatment options, and preventing the spread of infection.
Causes
The primary causes of scabies include:
- Mite Infestation: The Sarcoptes scabiei mite burrows into the skin and causes irritation.
- Close Contact: Direct physical contact with infected individuals allows scabies to spread easily.
- Sharing Personal Items: Using shared towels, clothing, or bedding increases the risk of infection.
- Poor Hygiene: Insufficient cleanliness raises the likelihood of mite transmission.
- Weakened Immune System: Individuals with compromised immune systems are more susceptible to scabies.
Symptoms
Scabies typically presents with the following symptoms:
- Intense Itching: Severe itching, particularly at night, is a hallmark symptom.
- Skin Rashes: Small red bumps or swellings develop on the skin.
- Burrow Lines: Thin, thread-like burrow marks may appear on the skin.
- Sores and Secondary Infections: Excessive scratching can lead to sores and secondary bacterial infections.
- Skin Thickening: Chronic cases may result in thickened and hardened skin.
Treatment Options
Effective scabies treatment includes:
- Topical Medications: Prescription creams like permethrin effectively kill the mites.
- Oral Medications: Severe cases may require oral antiparasitic drugs like ivermectin.
- Cleaning Personal Items: Clothing and bedding should be washed or dried at high temperatures.
- Home Hygiene Measures: Cleaning and disinfecting all surfaces in the home prevent further infestation.
- Itch Management: Antihistamines or corticosteroid creams help alleviate itching.
Prevention and Protection
To prevent scabies, follow these measures:
- Personal Hygiene: Regular handwashing and avoiding the sharing of personal items.
- Avoid Close Contact: Refrain from close contact with infected individuals.
- Clean Clothes and Linens: Regularly wash and dry clothing and bedding at high temperatures.
- Education and Awareness: Understanding scabies symptoms and transmission helps reduce the risk of spread.
Skin Care and Lifestyle
Proper skin care and a healthy lifestyle are essential for managing scabies:
- Gentle Cleansers: Use hypoallergenic cleansers to avoid irritating the skin.
- Moisturization: Regular moisturizing protects the skin barrier and supports healing.
- Balanced Nutrition: A diet rich in vitamins and antioxidants strengthens the immune system.
- Adequate Sleep: Sufficient sleep contributes to the body’s healing processes.
- Reduce Smoking and Alcohol Consumption: These substances can weaken the immune system and increase infection risk.
- Stress Management: Techniques such as meditation, yoga, and breathing exercises support overall health and immune function.
Appointments and Contact
For more information on scabies and expert advice, please contact us. Restore your skin health and comfort with the expertise of Associate Professor Tuğba Falay Gür.