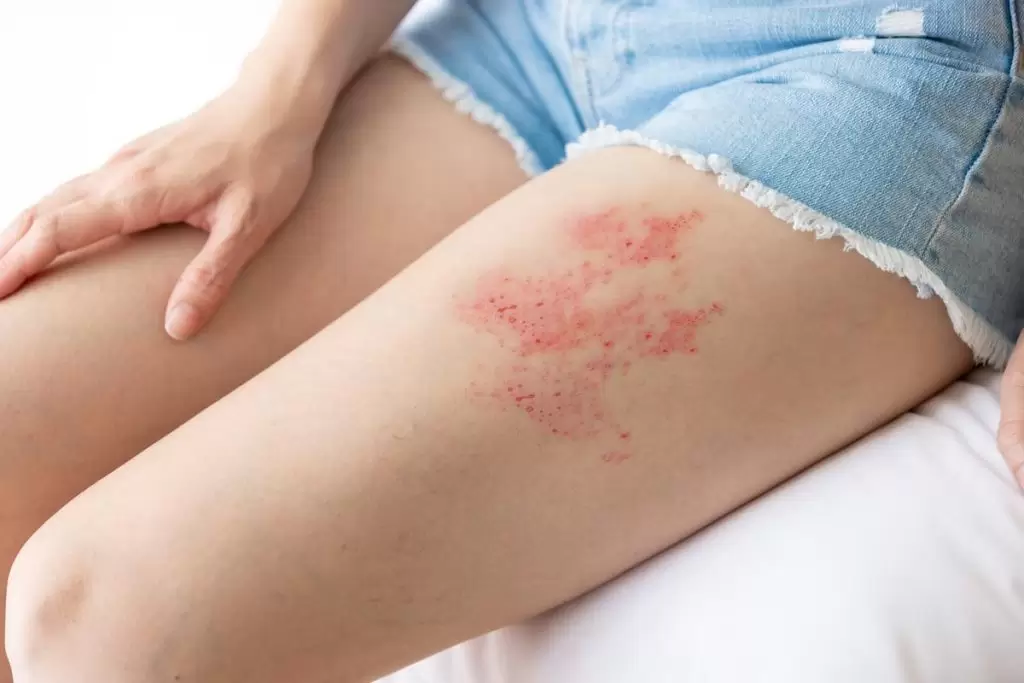
Shingles, or herpes zoster, is a painful viral infection caused by the reactivation of the Varicella-Zoster Virus (VZV), typically during periods of weakened immunity. Associate Professor Tuğba Falay Gür specializes in understanding the causes of shingles, providing effective treatment options, and preventing complications.
Causes
Shingles occurs when the dormant VZV, which causes chickenpox in childhood, reactivates in the nerve cells. Factors contributing to this reactivation include:
- Weakened Immune System: Aging, stress, cancer treatments, and conditions like HIV/AIDS weaken the immune system.
- Age: More common in individuals over 50.
- Stress and Psychological Pressure: Chronic stress can trigger the virus’s reactivation.
- Surgical Interventions: Temporary immune suppression after surgeries.
- Chronic Illnesses: Conditions like diabetes that affect immune function.
Symptoms
Shingles often manifests with the following symptoms:
- Painful Sensations: Burning, stabbing, or severe pain, often localized to the torso or face.
- Skin Rashes: Red rashes and blisters develop in the affected nerve region.
- Itching and Burning: Itching and burning sensations accompany the rash.
- Fatigue and Weakness: General fatigue and malaise may occur.
- Fever and Headache: Mild fever and headaches in some cases.
- Nerve Complications: Rarely, postherpetic neuralgia, characterized by long-term pain, may develop.
Treatment Options
Shingles treatment includes various methods:
- Antiviral Medications: Drugs like acyclovir, valacyclovir, and famciclovir inhibit viral replication and shorten the healing process.
- Pain Management: NSAIDs and opioid derivatives can help reduce pain.
- Topical Treatments: Lidocaine creams or capsaicin ointments alleviate pain and itching.
- Corticosteroids: Oral or topical corticosteroids reduce inflammation in severe cases.
- Postherpetic Neuralgia Treatment: Antidepressants, anticonvulsants, and local anesthetics help manage chronic pain.
- Physical Therapy: Supports pain management and maintains mobility.
Prevention and Protection
Preventive measures for shingles include:
- Vaccination: The shingles vaccine significantly reduces the risk, especially in individuals over 50.
- Strengthening the Immune System: A balanced diet, adequate sleep, regular exercise, and stress management support immunity.
- Hygiene: Frequent handwashing and avoiding sharing personal items prevent spread.
- Healthy Lifestyle: Avoid smoking, limit alcohol consumption, and adopt a general healthy lifestyle to support the immune system.
Skin Care and Lifestyle
Proper skin care and lifestyle play crucial roles in managing shingles:
- Gentle Cleansers: Use hypoallergenic products to avoid skin irritation.
- Moisturization: Keep the skin hydrated to support healing and reduce discomfort.
- Adequate Nutrition: Consuming foods rich in vitamins and antioxidants boosts immune function.
- Regular Sleep: Sufficient rest aids the body’s healing processes.
- Reducing Smoking and Alcohol: These substances weaken the immune system and increase infection risk.
- Stress Management: Techniques such as meditation, yoga, and breathing exercises enhance overall health and immunity.
Appointments and Contact
For more information on shingles and expert advice, please contact us. Achieve a healthy and comfortable life with the expertise of Associate Professor Tuğba Falay Gür.