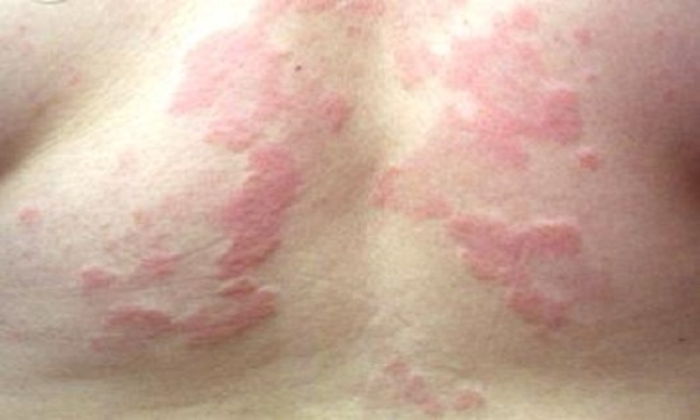
Urticaria, commonly known as hives, is a widespread dermatological condition characterized by sudden onset of itchy, red welts on the skin. Associate Professor Tuğba Falay Gür specializes in identifying the causes of urticaria, providing effective treatment options, and improving patients’ quality of life.
Causes
Various factors contribute to the development of urticaria:
- Allergic Reactions: Foods, medications, insect bites, or latex are common allergens triggering urticaria.
- Medications: Antibiotics, aspirin, and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can cause hives as a side effect.
- Infections: Viral, bacterial, or fungal infections can lead to infection-induced urticaria.
- Stress: Psychological stress can affect the immune system, triggering urticaria.
- Physical Factors: Temperature changes, pressure, sunlight, or cold exposure may contribute to hives.
- Autoimmune Diseases: Certain autoimmune conditions may lead to chronic urticaria.
- Genetic Predisposition: Individuals with a family history of urticaria are at higher risk.
Symptoms
Urticaria typically presents with the following symptoms:
- Itchy Welts: Sudden appearance of itchy, red bumps on the skin, usually 1-5 cm in diameter.
- Red Rash: Redness around the welts.
- Migrating Lesions: Welts that appear to move toward the center.
- Skin Swelling: Swelling in areas affected by bites or welts.
- Mild Fever: Occasionally accompanied by a low-grade fever.
- Skin Changes: Prolonged urticaria may cause permanent discoloration or textural changes.
Treatment Options
Several methods are available for managing urticaria:
- Antihistamines: Oral antihistamines (e.g., loratadine, cetirizine) relieve itching and reduce rash.
- Corticosteroids: Short-term use of corticosteroids may be prescribed for severe cases.
- Topical Creams: Hydrocortisone creams reduce inflammation and alleviate symptoms.
- Immunomodulators: Chronic urticaria cases may benefit from medications that regulate immune responses.
- Avoidance of Triggers: Identifying and avoiding specific triggers helps manage the condition.
- Cold Compresses: Soothing cold applications alleviate itching and swelling.
- Stress Management: Techniques such as yoga, meditation, and breathing exercises prevent flare-ups.
Prevention and Avoidance
To prevent urticaria, consider these measures:
- Avoid Allergens: Reduce exposure to identified allergens to prevent flare-ups.
- Skin Care: Use gentle cleansing products and keep the skin moisturized to protect the skin barrier.
- Sun Protection: Apply broad-spectrum sunscreens to shield the skin from harmful UV rays.
- Healthy Lifestyle: Balanced nutrition, adequate sleep, and regular exercise strengthen the immune system.
- Stress Reduction: Engage in stress-relieving activities to minimize triggers.
- Medication Review: Monitor medication side effects and discuss concerns with a doctor.
Skin Care and Lifestyle
Effective urticaria management relies on proper skincare and a healthy lifestyle:
- Gentle Cleansers: Use hypoallergenic cleansers to avoid skin irritation.
- Moisturization: Regularly hydrate the skin to maintain its barrier and alleviate itching.
- Balanced Diet: Consume foods rich in vitamins and antioxidants to support the immune system.
- Regular Sleep: Adequate rest aids the body’s healing processes.
- Reduce Smoking and Alcohol Consumption: These substances may impair the immune system and exacerbate symptoms.
- Stress Management: Practices like meditation, yoga, and breathing exercises support overall health and immunity.
Appointments and Contact
For more information about urticaria and to receive expert guidance, please contact us. Relieve discomfort and maintain healthy skin with the expertise of Associate Professor Tuğba Falay Gür.